 |
 |
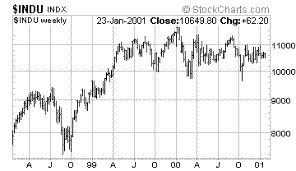
| Dow
Jones Industrial Average |
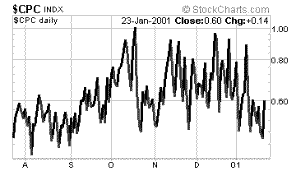
Put
/ Call Ratio -- suggesting too much optimism |
The next
2,000 points is now down,
That would be the Dow Jones Industrial Average that we are
talking about, and we will certainly show you why we see
that outcome, but also, we would like to offer up a little
bit of truth about the "economy."
Fed fuels
consumption as inflation risks accelerate:
Consumption is our economy and credit money drives it, but
what backs it? A mountain of paper denominated assets? A
strong dollar "policy?" Productivity? Economic growth? How
about none of the above. We've seen how well paper assets
hold up, but that was nothing. Wait until this year is through.
As for policies, few are assembled without fault. The strong
dollar policy can only work so long as the inflation is
containable - in other words, so long as it still works
to inflate paper rather than to devalue the purchasing power
of the currency - and only so long as there is cooperation
among the major currency partners, which is often the outcome
of shared interests. We discussed this in the last issue
(Dollar/Yen=Dollar/Gold).
What
of productivity? There have been some highly intelligent
thoughts on the validity of the Fed's productivity argument.
Dr. Frank Shostak posted a thorough overview of the delusion
behind much of the data (The
Labor Productivity Myth), as have others, and we've
already covered the subject ourselves in the summer time.
Please refer to A
Nation of Storytellers.
The
delusion begins with a fundamental misunderstanding between
money supply and economic growth, as measured by the GDP,
GNP, or what have you. The fact is that the statistic that
we are familiar with as Gross Domestic Product is in reality,
only a measure of the money supply. Please refer to Dr.
Shostak's case as our reference for this, and for the sake
of brevity here. It is really important to understand that
what we qualify as economic growth is effectively a credit
induced expansion in the money supply, which tends to expand
only when the horses still choose to (or can) drink the
generously supplied water.
At
the core, productivity is total output per hour of
labor, which goes into producing the output. But
by using our national income statistics, this number simply
divulges the total amount of money spent per hour of work.
And although that number has been rising, it has taken ever
more credit money to influence each dollar of actual expenditure
(consumption). I
guess that the rest goes to servicing our rising "aggregate"
debt levels, or to other non-productive wealth redistributing
activities.
I
am indeed suggesting that money, which is not somehow
spent "efficiently," is less likely to show up in the
final output number, which "leak" must be either the symptom
of an overzealous credit expansion or an impotent monetary
policy. Another way to say that is that there are patterns
of consumption that work well to maximize that output
number, and there are patterns of consumption that work
against it, specifically the kind that result in an immediate
decline in the purchasing power of the currency. Additionally,
the potency of monetary policy can in many cases influence
these patterns of consumption as easily as any other deliberate
program.
Nevertheless,
our increasing leak should continue to erode the effectiveness
of monetary policy at the Fed, and as the effectiveness
of monetary policy erodes, so too, will the (above) productivity
number ultimately decline. But it doesn't stop there, our
ignorance that is.
It
has understandably become important for us to understand
how much real money it costs to produce a level of real
output in an hour. So, perhaps in order to acknowledge that
total output measured in dollars (the unit of account in
this case) is only a monetary output statistic, the concept
of nominal and real GDP is introduced into the argument.
Yet the adjustment is arbitrary, because it is only a government
estimate of how much purchasing power the money has lost.
Still, this arbitrary number helps them arrive at what is
a more generally acceptable measure of real economic performance.
Anyhow,
the whole idea that the measure of productivity imparts
what many "experts" say it does is nonsense. Our hope is
that we can help explain why it doesn't.
So, if productivity
= real hourly output / hourly unit labor costs, then…
Having
considered the numerator, let us also assure you that the
denominator, the unit cost of labor per hour, is also a
mish mash (sum) of mutually exclusive variables… like adding
apples to oranges and saying that you have got two apples.
But, does that mean that the equation (above) is meaningless?
It is arbitrary in its most common interpretation, but not
entirely meaningless. Then what does it tell us and who
is it most useful to?
Calculated
this way, the productivity data tells us how much (arbitrarily
adjusted) money we can create per hour of work, and if we
can do it profitably, thus efficiently. Then we can compare
the data to last week, last month, or last year, in order
to determine if our country is printing and spending this
money with greater "efficiency" or not. In other words,
if this number is high, then inflationist monetary policies
can still work - as opposed to break down.
Thus,
productivity (calculated this way) is simply a measure of
the productivity of inflation. Obviously, this is a meaningful
statistic for a central banker to have.
An example
For instance, imagine an economy where the top number (total
adjusted money supply spent per hour) divided by the
bottom number (hourly monetary compensation) results
in a number, which ultimately defines your nation's economic
standing and therefore, economic purchasing power. Assume
that you, being a powerful world leader, want to maximize
that number.
All
you would need to do is encourage consumption (sort of like
persuading the horse to drink water from the trough) and
therefore credit, thereby increasing the supply of money.
Now,
the trick is to ensure that the money is not spent on real
things, all at once. Rather that the bulk of the excess
money supply is poured into the asset markets, preferably
the paper asset markets, so that more credit can be created.
This way there is a positive drag on the reported inflation
rate, which then influences (discovers) a maximum value
for the numerator. And in such an economy, where the asset
markets can generally inflate at will, foreign investors
are attracted to this "productive" inflation, are willing
to finance its perpetuation, and effectively encourage the
cycle of consumption by inflating our global economic purchasing
power (by bidding up the value of dollars).
In
such an economy, what employee would turn down the lure
of the stock option to cash? Remember, in this economy,
stocks go up at will. Anyhow, if enough participants (people)
do choose this method of remuneration, conceivably, the
effect would be to depress the denominator in our equation.
Thus, the productivity rates in our hypothetical economy
would surely rise.
But
what if one day, stocks do not go up anymore? What employee
is going to prefer a stock option plan to cash? And if wages
begin to rise as a result (of many things really), will
not the denominator in our equation be forced higher?
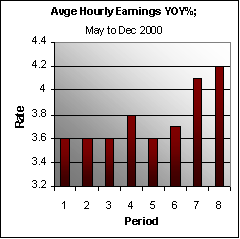
That
is where we are. The future of our economic delusion rests
with the effectiveness of monetary policy. But total stock
market capitalization has not been able to expand for well
over a year, even though the Fed has allowed, and encouraged,
the monetary aggregates to grow wildly throughout this period.
So if people are not buying stocks with this new money (liquidity),
and they continue to lose confidence in the increasingly
abundant paper, what might happen in our simple economy?
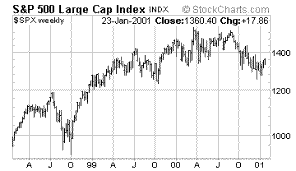 |
 |
| S&P
500 Stock Index |
Most
commonly used measure of Money Supply
|
Participants
may stop saving altogether and spend all of this never-ending
supply of credit money on real things, rather than on stocks.
So, the top number becomes smaller now, well, as soon as
the lag in the government statistic (the price deflator
/ CPI) is washed out, that is. And if the process continues
to be fueled by a cowboy Fed policy, it will prompt accelerations
in the reversion to an objective valuation for the dollar.
 |
 |
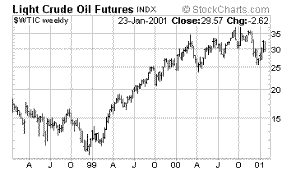
| West
Texas Intermediate Crude |
Most
commonly used measure of Money Supply
|
Thus,
taking all of this into account, we too will join the growing
chorus of analysts "predicting" that the US productivity
data will begin to decline, except that we think the number
will decline for some time. The reason is because we fully
suspect that the inflationist policies of the Fed have been
breaking down, terminally. Therefore, we also predict that
the purchasing power of the dollar will continue to erode,
against most things, and until the foundations of excess
are purged. So you see, the number does mean something to
us, but it also means something to the Fed Chairman.
Mr.
Greenspan's productivity edict is intended to mean that
he assures us, and believes, that the inflation can still
work. That monetary policy is still effective. As long as
productivity rates rise, the inflation can still work, and
so, every time Mr. Greenspan lowers the interest rate, stocks
will rise on command!
So, what
are they buying, besides oil?
Since the last rate cut early this month, investors have
been piling into the high yield, high risk securities markets,
allowing some of the liquidity starved financial houses
to reduce their risk, and perhaps walk the stock markets
up a little bit more. Survival of the fittest my ass; this
type of socialist monetary system can only reward the biggest
and dumbest fools. Accordingly, it is doomed.
An economic
slowdown, or an "inflation" warning?
 |
 |
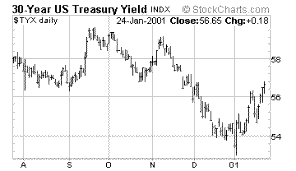
| US
30 Year Government Treasury -- long bond |
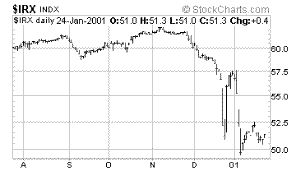
CBOE
Short Term Yields -- Index |
What
these two charts mean is that long-term interest rates are
going up and short-term interest rates are going down. Simple,
huh? Whether the analyst interprets this chart as a sign
that a short recession may be behind us now (and that the
yield curve is thus simply normalizing), or that inflation
expectations are on the rise, will depend on his or her
understanding of what inflation actually is.
If
inflation is (interpreted as) the result, on the general
"price level," of some form of aggregate economic demand
exceeding some contrived concept of total economic capacity,
then the analyst will tell you that the normalizing yield
curve is the result of a slackening in demand, and further,
that it (the curve) is predicting the end of the economic
weakness, and ultimately setting up for a turnaround. But
this form of analysis overlooks the real possibility that
prices may rise even as "aggregate" demand (consumption)
weakens. That is because the analysis refuses to take into
account the influence of individual preferences on the purchasing
power of the money used in any given transaction, at any
specific moment in time.
If
the analyst is driven by the truth, however, he (or she)
will understand that the concept of a price level means
adding apples to oranges to a pair of jeans to an automobile
in order to arrive at an average that is representative
of something too meaningless to qualify as abstract, in
the first place. This analyst should then also realize that
the one thing, which these very different things do have
in common, is the money in which they are priced (exchanged
for). Thus, the quantity of money combined with
an individual's unique preferences, at any given moment,
will determine the value of that money, and thus the price
of a specific good.
Furthermore,
the analyst will know that the lower short-term interest
rate is not only an artificial policy induced rate, but
that it will ultimately fuel the inflation. Unfortunately,
this is a result that comes nowhere near describing an economic
trough, but rather a continuing crisis. Let's keep it simple,
shall we?
When this
is happening, it is a really bad idea to lower interest
rates!
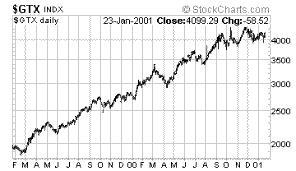
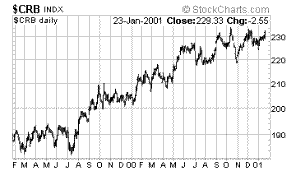 |
 |
| Commodity
Research Bureau Index |
Goldman
Sachs Commodity Index -- Total Return |
Why?
Because when people become confused about the value of things,
which they so often do, and their central bank keeps throwing
new (credit) money at them, they will in turn throw it in
the direction that suits their economic interests. Thus,
the meaning of the phrase, liquidity seeks inflation.
And if the system arrives at the point where everybody is
cashing in his or her chips because nothing else is inflating
anymore, the inflation that has been so well managed and
organized, will become disorganized. Government policies
will beget bad ones, as they have no choice but to defend
the value of the (overly issued) currency with everything
that they have got, which never is enough when it comes
to a war over real things, and the entire economy implodes.
Not
even higher interest rates can stop this process when it
gains momentum. Only the hoarders will make money. But so
be it… the social consequences of dishonest money.
Again,
we post these two charts as we did in late December, and
we ask Mr. Greenspan to please lower interest rates again…
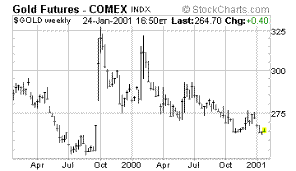
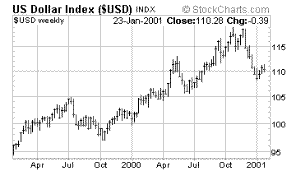 |
 |
| US
Dollar Index |
COMEX
Gold Futures -- Note the declining wedge |
We
did ask nicely, didn't we?
Nostalgia
Mr. Greenspan has now had two different occasions to reflect
on the Greenspan-Put. The first being just before Christmas
time when he made the original promise. The stock market
yawned. The second when he tried to catch the market entirely
by surprise, and did, on January 3rd, with a half point
credit sale. The move has worked to alleviate some credit
market stress, but otherwise, has not done much for the
stock or government bond market. What if the next one doesn't
work either? Well, that is one basis for our stock market
call, for the next one is already priced into the Fed Funds
market - the rumor having already been floated during Tuesday
morning's trading session.
Dollar
confidence will then have to rest with a leaky (leaking
inflation everywhere except in the government figures) dollar
and fiscal policy? Yikes. So, get this, and I hope you are
sitting down for this.
We are so
insolent…
Mr. Greenspan's upcoming testimony
is going to have to hint at a reverse course in monetary
policy. He is going to have to reflect on the risks to inflation
of engaging a monetary policy that is perceived to be the
cure for our economic problems, when it is actually the
cause. He will have to, sooner or later, admit that monetary
policy, while effective under conditions in the past, is
no longer effective. Of course he will. For, if every time
that interest rates are lowered, the new liquidity increasingly
fuels the prices of real things (read: accelerates the point
of recognition), then it will also accelerate the rate of
deterioration in the purchasing power of the dollar.
Who
am I kidding? Yet, this kind of talk is the only way to
make US monetary policy effective again. Here is why: First,
because it would unquestionably knock the heck out a stock
market, which is expecting lower interest rates. And then,
maybe then, a 50 basis point rate cut can work to re inflate
the stock market… maybe. For the record, Mr. Greenspan already
made his first mistake by not listening to us when we suggested
(in December) that he shouldn't lower interest rates until
after the stock market sells off.
Anyhow,
even if he were to talk the talk, I know it cannot possibly
sound quite as honest as written above, but the point is
only incidental anyways… not a serious prediction, more
like a guess, a gut guess. But consider some of our more
logical support for the stock market call.
The Sensitivity
Index
Oil prices, on the other hand, have indeed acted on command.
They have risen 15% since the rumor of an OPEC cut was first
floated. This is an important observation for any trader
because just by comparing the stock market response to an
interest rate cut with the response of oil prices to an
OPEC cut announcement, you have found your real bull market!
If this doesn't make sense, consider it this way.
If
two public companies concurrently announce better than expected
earnings, assuming all else being equal, and one's shares
react (rise) stronger than the other, in the market, you
could make dumber mistakes than to assume that it was the
right one to buy.
What else
we do not like about this "stock" market…
The blue chip averages, Dow Industrials and NYSE composite,
look poised for another crack at support. Both spent the
short week bumping up against their 200 day moving averages,
but in the end, couldn't cut it, closing Friday's session
in disappointment, near the low end of the trading week.
The action so far this week has changed nothing.
In
December, we suggested that the Nasdaq was ripe for a bounce,
but we also concluded that the bounce would presage a crash
in the blue chip averages, as it would crowd out the remaining
liquidity. The Fed responded by slashing interest rates
in order to provide additional liquidity, thus delaying
the move. Early last week, we thought the bulls had enough
time to gather momentum and concluded that if they didn't
demonstrate any meaningful territory, the bear would reassert
its position shortly thereafter. On Tuesday morning, rumors
that Mr. Greenspan was going to hint at a minimum 25 basis
point cut at his testimony, on Thursday, sent the equity
markets on what may have been their last gasp.
A
glance at yesterday's Dow leadership was revealing. The
top quartile of performers included General Electric, American
Express, Boeing, Coca Cola, Home Depot, Intel, and International
Paper. Below is a brief overview of the technical (chart)
condition of each stock. The top 7 performers all rallied
over 2% on Tuesday January 23rd:
General
Electric,
Recently
broke down from a 10 month Head and Shoulder top, which
has been tested twice now, and thus implies a $12 drop to
$34 from here, give or take. The objective is roughly a
25% decline. Today's pop may have been its last test of
resistance at $47.
American
Express
AXP has seen an enormous amount of selling pressure impressed
upon a long in the making sagging top of various persuasions
(multiple bearish technical patterns) almost on the very
same day that the Fed slashed interest rates. Volumes almost
classically accelerated into the decline. On Tuesday, AXP
exhibited climactic behavior, but prices traded mostly an
inside day. The market is only half way to its more obviously
immediate objective at $40, another $6.50 from here (12%
lower). This move is not over, and besides, volume climaxes
often precede a turn around in price, sometimes by a week
or two.
Boeing
This stock may be in the process of topping out right now.
Money flows have turned decidedly against the bulls here
(since early December), and prices may have conceivably
fallen out of a small two-month rising wedge. But while
the stock price has not yet clearly broken down, in my opinion,
it has yet to establish an intermediate higher low, also,
in what may become a primary bull trend. What that means
is that it has yet to test trend support at $54, and then
that has yet to prove that that was trend support. In other
words, there is plenty of nearby downside.
Coca
Cola
Money flows have turned bearish now (meaning that over the
past twenty days, on average, the higher volume days are
down days - typically a sign of distribution) after three
discernibly noble attempts (?) to turn the primary trend
around, which remains bearish, at the $64 handle. This chart
had the potential for a turn around, but the bears have
visibly demonstrated primary trend control and arguably,
now appear ready to test the $50 low, $7 (12%) lower.
Home
Depot
HD is simply a terrible looking chart. The bears have a
lot of unfinished business here. The October break down
confirmed a double top, which straddled the beginning of
last year (2000), while December's rally filled a gap, retested
the validity of that same top, and established a potential
downtrend. Thus, the stock appears ready to test the $34
level again, in the short term (almost a 24% decline).
Intel
The stock has room to move higher, but unquestionably, only
within a primary down trend. After testing the low $30 handle
for bullish support, repeatedly, over the course of January,
the bulls moved the stock back up to the $35 mark. A run
at the bearish outpost somewhere near the $40 level is not
out of the question, but confidence is paramount.
International
Paper
IP is a stock where the money flows have turned decidedly
in the bulls favor. December's accumulation was so heavy
that it established a powerful correction to the bearish
primary trend. But that is all. The primary bear trend is
still intact. Thus, if that is correct then there is room
for new lows, but the relatively strong signs of accumulation
may also foretell of the kind of leadership this market
may get in the next cycle, perhaps late this year. Yet,
even if that is true, a successful retest of October's lows
may still be in the cards if only to establish a long term
bottom. Still, that is about 30% lower.
Conclusions
Except
for Intel, Tuesday's interest rate rumor did little to alter
the bearish bias in any of the above leadership. If anything,
it set up the next down leg.
The
Nasdaq indexes spent the short week (last week) rising in
countertrend, but bumped up against the bearish stronghold
just a little too hard and ended up gasping for more air
by the time they got there. It was a 150-point rally on
the week, at best. Volumes weren't bad at all for the week.
We
could hear the bulls snorting away and aching to go all
week long, still in denial of the forces, which have already
turned the primary trend against them. Can they make it
to 3000 (another couple of hundred points or more)? Possibly,
but can they make it to 3500? That is what they will have
to do to turn this market around.
But,
you might ask, that's a pretty good rally... up 25% from
here? It is, but for a market (index at that) to rise by
25%, it has to "look" like it can rise a lot further than
that. That said, they (bulls) did manage to leave behind
a 500 point one month diamond (a popular pattern this month)
and push through the faster 50 day moving average, raising
the odds for a short spurt to the 3000 handle on a day when
the bears aren't looking.
The
move, in fact, may be just what the doctor ordered to create
the next liquidity crisis for the Fed. Thus, the stock market
is a sell.
 |
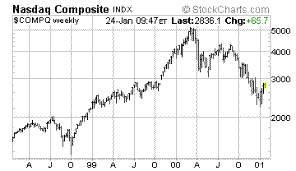 |
| Dow
Jones Industrial Average |
Nasdaq
Composite Stock Index |
Sincerely,
Edmond J. Bugos
The GoldenBar Global Investment Climate is not a
registered advisory service and does not give investment
advice. Our comments are an expression of opinion only and
should not be construed in any manner whatsoever as recommendations
to buy or sell a stock, option, future, bond, commodity
or any other financial instrument at any time. While we
believe our statements to be true, they always depend on
the reliability of our own credible sources. Of course,
we recommend that you consult with a qualified investment
advisor, one licensed by appropriate regulatory agencies
in your legal jurisdiction, before making any investment
decisions, and barring that, we encourage you toconfirm
the facts on your own before making important investment
commitments.
|